This discussion is now closed.
Check out other Related discussions
- I'm unsure of what to do for my Physics Research Project/Report Project (OCR A A2))
- Is this fair
- Optical fibres
- Virgin/O2 Technology Placement - Virtual Assessment and embarrassing question
- I'm losing the magic...
- alcohol and bowel issues
- Does anyone want to study the optical software?
- Anyone know if the Laptop provided
- Does Anyone have Experience of the Conversion Course at Bradford?
- Biology question cellulose
- Another a level chem question that makes zero sense, help please!
- Constipation problems
- A level organic MC
- Complex ions and optical isomer question help please :)
- trasnferring into optometry degree
- Why am I constipated ?
- Irregular bowel movements
- A level chemistry optical isomerism MC questions
- side effects on the pill
- Jeremy Hunt to deliver budget on March 6 as election looms
Fibre optics
Ok so here's what i know
-Higher the refractive index the slower the speed of the wave in that medium.
-Inner core has a high refractive index, the cladding has a lower index.
-TIR happens when i+r is greater than the critical angle.
Need it explaining really, diagrams always help. I've got two parallel lines and the normal perpendicular to them, need a definition of the critical angle and what value must the angle of incidence be over for total internal reflection to occur... and also, is some of the light always refracted as well as reflected? TOTAL IR would imply not, just checking
Thanks
-Higher the refractive index the slower the speed of the wave in that medium.
-Inner core has a high refractive index, the cladding has a lower index.
-TIR happens when i+r is greater than the critical angle.
Need it explaining really, diagrams always help. I've got two parallel lines and the normal perpendicular to them, need a definition of the critical angle and what value must the angle of incidence be over for total internal reflection to occur... and also, is some of the light always refracted as well as reflected? TOTAL IR would imply not, just checking

Thanks
Total internal reflection happens when the refraction angle no longer makes any sense, at least not in the classical sense.
Snell's Law defines the angle of defraction.
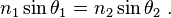
If you concider this equation, you can see at some point there are conditions where sin theta > 1. Which obviously can not be true.
Snell's Law defines the angle of defraction.
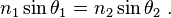
If you concider this equation, you can see at some point there are conditions where sin theta > 1. Which obviously can not be true.
Not really what i was after  AS level...
AS level...
I tried to use that equation to solve a problem, want to know angle of refraction...
air refractive index 1, glass 1.5
i=incidence,r=refraction
n1 x sin i = 1.5 x sin r
1 x sin23 = 1.5 x sinr
0.390731128 = 1.5 x sinr, rearange to ANS/1.5=sinr
Help!
 AS level...
AS level...I tried to use that equation to solve a problem, want to know angle of refraction...
air refractive index 1, glass 1.5
i=incidence,r=refraction
n1 x sin i = 1.5 x sin r
1 x sin23 = 1.5 x sinr
0.390731128 = 1.5 x sinr, rearange to ANS/1.5=sinr
Help!
Related discussions
- I'm unsure of what to do for my Physics Research Project/Report Project (OCR A A2))
- Is this fair
- Optical fibres
- Virgin/O2 Technology Placement - Virtual Assessment and embarrassing question
- I'm losing the magic...
- alcohol and bowel issues
- Does anyone want to study the optical software?
- Anyone know if the Laptop provided
- Does Anyone have Experience of the Conversion Course at Bradford?
- Biology question cellulose
- Another a level chem question that makes zero sense, help please!
- Constipation problems
- A level organic MC
- Complex ions and optical isomer question help please :)
- trasnferring into optometry degree
- Why am I constipated ?
- Irregular bowel movements
- A level chemistry optical isomerism MC questions
- side effects on the pill
- Jeremy Hunt to deliver budget on March 6 as election looms




