GCSE C1 CHEMISTRY AQA UNOFFICIAL MARK SCHEME 18th MAY 2017
Hey guys, today's depressing... Even thought the paper was of amateur difficulty, I decided not to acknowledge that the equation was changed by the - crafty, to say the least - board. Therefore I lost 2 marks there. But here's the mark scheme you've all waited for:
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
Differenr number of neutrons eg B had more than A(use the table)
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
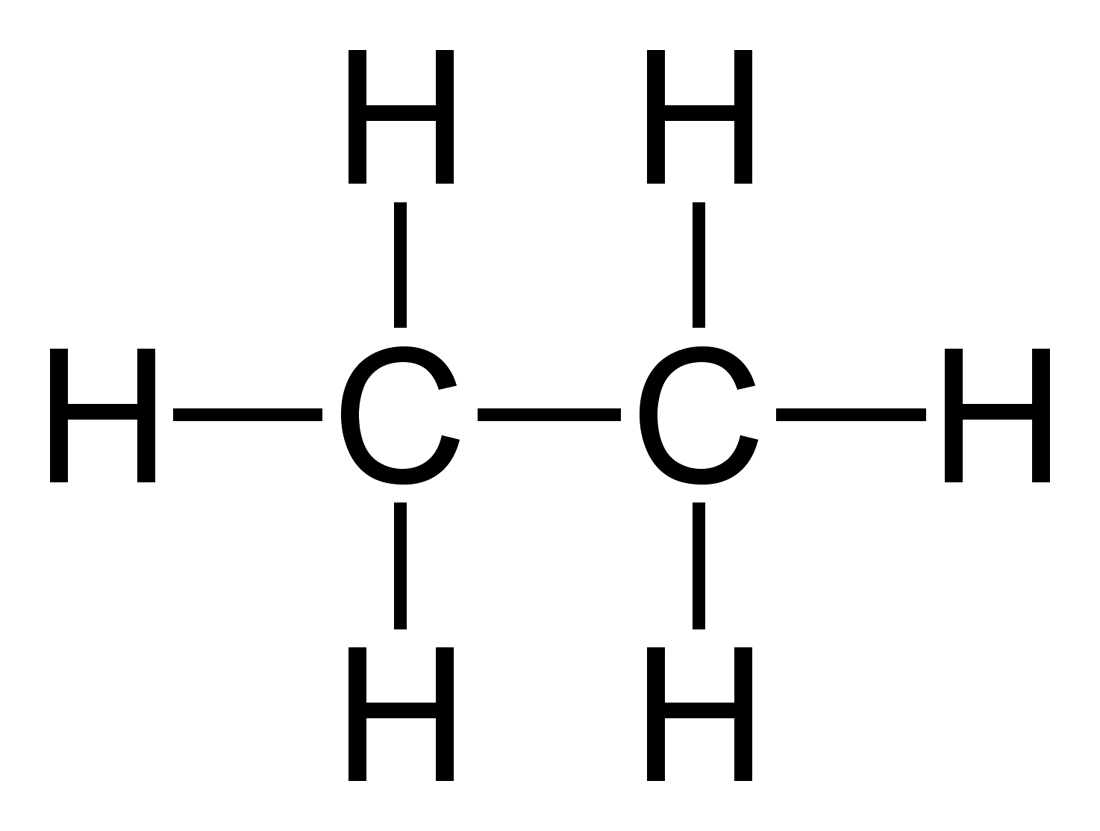
2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps )
)
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
Differenr number of neutrons eg B had more than A(use the table)
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
Attachment not found

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps
 )
)(edited 6 years ago)
Scroll to see replies
Well according to this i did quite good 
Thanks

Thanks
i wrote that a hydrocarbon is 'a compound of hydrogen and carbon (mostly)' because i got mixed up, the definition is actually 'only'
do examiners still mark something in brackets s i won't get the mark?
do examiners still mark something in brackets s i won't get the mark?
Original post by mahmed69
Hey guys, today's depressing... Even thought the paper was of amateur difficulty, I decided not to acknowledge that the equation was changed by the - crafty, to say the least - board. Therefore I lost 2 marks there. But here's the mark scheme you've all waited for:
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps )
)
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
Attachment not found

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps
 )
)Im sure that 2bi you need to to talk about cracking. Look in your textbooks.
2a also got to me lol
lol I ****ed up
His mark scheme is fake; here's the real one.
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
Attachment 648492
2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
Attachment 648492

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
What do you predict the grade boundaries will be???
Original post by mahmed69
Hey guys, today's depressing... Even thought the paper was of amateur difficulty, I decided not to acknowledge that the equation was changed by the - crafty, to say the least - board. Therefore I lost 2 marks there. But here's the mark scheme you've all waited for:
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps )
)
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
Attachment not found

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps
 )
)What about the Foundation paper? I can't find he Unofficial Markscheme for that

oi mo could i have said hydrogen reacts instead of joins the chain
According to this I got 40, what grade would you guess that to be?
Original post by mahmed69
Hey guys, today's depressing... Even thought the paper was of amateur difficulty, I decided not to acknowledge that the equation was changed by the - crafty, to say the least - board. Therefore I lost 2 marks there. But here's the mark scheme you've all waited for
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps )
)
1ai) complete the carbon atom. [1]
2 in inner, 4 in outer
1aii) explain in terms of subatomic particles why the atomic number is the same. [1]
all have same number of protons
1bi) explain in terms of subatomic particles, why the atoms have different atomic masses. [2]
1bii) complete the sentence: [3]
the central part contains 6 neutrons with no electric charge and 6 protons with a 1+ charge, so over charge of nucleus is positive
1c) how many elements in H2SO4? [1]
3
1d) How many atoms in H2SO4? [1]
7
2ai) tickbox: 159g of copper oxide reacts with 196 grams of sulphuric acid, whats the mass of the products? [1]
bottom box: 319 and 36
the following question is retardid
2aii) THIS GOT ME THEY CHANGED THE F*ING EQUATION:
Copper carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid. (apparatus shown), describe and explain the changes you would see. [3]
copper sulphate salt would form In conical flask because copper would displace the SO4. Mass reading on scale would decrease as CO2 would escape into test tube. this would cause limewater to turn cloudy. there may also be effervescence and bubbles as CO2 is produced.
2bi) describe what would happen to the alkanes in the liquid paraffin. [3]
thermal decomposition reaction happens. this means heating it vaporises the alkanes, they pass over catalyst and break to form smaller more useful hydrocarbons and so they collect as gas in the top of the test tube.
2bii) what's a hydrocarbon? (correct me if im wrong) [1]
molecule of hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
2c) draw ethene and ethane [2]
Attachment not found

2di) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points of alkanes [1]
more carbon atoms means higher boiling point
2dii) describe the differences between the boiling points of alkenes and alkanes(data given) [2]
alkenes generally have lower boiling points, eg. hexane has BP of 68 degrees but hexane(or something) is 64 degrees. (if u used data ur fine)
3) 6 MARKER ON LIMESTONE(BLESs!) explain the environmental impacts from quarrying, drilling and thermal decomposition [6]
quarrying and explosions destroy animal habitats and also scare away animals, reducing biodiversity. may also cause dust and noise pollution. thermal decomposition releases CO2, causing global warming to increase. SO2 released may cause acid rain, and the nitrogen** released may react with the oxygen at high temp. causing nitrogen oxides to form, causing acid rain. the methane from drilling is also a greenhouse gas and very flammable, could explode. the drilling machinery may release co2 and other pollution.
** maybe?/? debatable I guess
4ai) describe the trends of plastic bag usage using data from figure [2]
shows sudden decrease from 2006, then shows gradual increase at a lower rate.
4aii) the data for mass of plastic bags doesn't support the data for bag usage, suggest two reasons why. [2]
I wrote for this; the trend ie. it decreased, then increased, and then decreased despite use of bags increased. this could be due to development of smart polymers and Low density polymers.
4aiii) what is polymerisation? [1]
lots of monomers join up to form long chain of monomers called a polymer
4bi) suggest and explain one reason why the bags should not be sent to landfill and reused instead. [2]
the don't break down easily(not biodegradable) so would stay there and use up lots of space
4bii) suggest two reasons apart from landfill why they should be recycled. [2]
recycling takes less energy than extracting and making polymers.
reserves crude oil resources which are non renewable
5ai) suggest why their experiment does not prove that amino acids were formed by the gases(something like that) [1]
they used the substances needed to make the glycine and not the substances that were actualy in the atmosphere
OR they didn't know what the actual gases were
OR they didn't use the CO2 or small traces of O2 in their experiment despite them being in the early atmosphere
5aii) describe three ways in which the amount of co2 in the atmosphere has decreased [3]
carbon sequestered/dissolved in oceans (largely).
locked up in sedimentary rocks (from shells of dead shelled creatures)
taken in by plants and algae by photosynthesis.
5bi) Why is CO2 during the process?[1]
freezes so would block up pipes etc
5bii) suggest which two gases do not condense when cooled to -200 degrees [1]
helium and neon
5biii) oxygen and another gas remain a mixture after distillation, explain why [2]
oxygen and ARGON have similar boiling points
5c) cast Iron is made in the blast furnace.
step 1; add oxygen to furnace, step 2; add other metals in small amounts.
suggest why these two steps are taken in the production of steel. [4]
oxygen reacts with carbon to remove it as this makes the iron brittle. This is released as CO2 from the furnace. more metals are added to make the pure iron harder and more useful as pure iron is too soft for use.
6a) Suggest and explain one advantage of using biofuels over fossil diesel. [2]
reserves resources so less crude oil is used up/extracted
6b) plant oils are used to make emulsions with water. explain how [4]
emulsifier is added to the oil and water, tail of emulsifier molecule is attracted to oil droplet so pushes way its into it. the head stays on the outside/surface as its attracted to water. this holds the oil droplet in the water, to keep a steady emulsion and provide the texture
6c) bromine water changes colour when some plant oils are added to it, describe the colour change [1]
orange-brown to colourless
6d) what happens to plant oils when they're reacted with hydrogen at 60 degrees with a catalyst? [3]
hydrogen joins the chain, and so double bonds break, giving it a higher melting point so doesn't melt at low temperatures ie RTP. this means its harder and has a spreadable consistency.
please comment below with any improvements. Much appreciated (don't forget to give reps
 )
)Original post by shaan 101010
oi mo could i have said hydrogen reacts instead of joins the chain
You have to say that the hydrogen opens up the double bonds into single bonds if u say that
Original post by Ewanross10
You have to say that the hydrogen opens up the double bonds into single bonds if u say that
yh said that
Original post by marie cool
What do you predict the grade boundaries will be???
Maybe be like
50-A*
43-A
35-B
I'm just assuming hopefully it's better
Original post by Btstrash
According to this I got 40, what grade would you guess that to be?
About 53 i guess
Original post by Princes blaire
i wrote that a hydrocarbon is 'a compound of hydrogen and carbon (mostly)' because i got mixed up, the definition is actually 'only'
do examiners still mark something in brackets s i won't get the mark?
do examiners still mark something in brackets s i won't get the mark?
No, on the official mark schemes produced by AQA, the information in brackets isn't needed to get the mark. However this is only the unofficial mark scheme so it doesn't actually mean anything. It is probable that you needed to say 'only' to get the mark. But hey - you never know

The grade boundaries will be about 53 for an a*
Original post by Fezza101
Maybe be like
50-A*
43-A
35-B
I'm just assuming hopefully it's better
50-A*
43-A
35-B
I'm just assuming hopefully it's better
Original post by Fezza101
Maybe be like
50-A*
43-A
35-B
I'm just assuming hopefully it's better
50-A*
43-A
35-B
I'm just assuming hopefully it's better
the mass changes because the plastic bags are getting smaller and are made up of lighter materials
Original post by Sammmyxxx
About 53 i guess
I dont get you there sorry? Do you mean that i got 53? I was asking cos i think i got 40, so would that be an A or a B?
Quick Reply
Related discussions
- GCSE Exam Discussions 2024
- gcse biology combined aqa 2023
- Aqa gcse biology paper 2 mark scheme 2023
- GCSE Exam Discussions 2023
- GCSE Mocks
- Please help
- A-level Exam Discussions 2024
- AQA GCSE Biology Paper 1 Foundation Tier [16th May 2023] Exam Chat
- AQA GCSE History Paper 1 (8145/1) - 18th May 2023 [Exam Chat]
- mark scheme biology 2022 gcse combined science higher paper 1
- REVISION - Y10 (GCSEs)
- Grade Boundaries - How far do they go up?
- AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 3 (7405/3) - 23rd June 2023 [Exam Chat]
- Arsey's solutions
- AQA A-level Biology 7402 - Paper 2 - 13th June 2019
- revision help :(
- Writing prompts in HK public exam
- Aqa biology a level paper 3 2023
- Edexcel A Level Economics A Paper 1 Unofficial Markscheme
- Oxford AQA International past papers 2018 & 2019 & 2020
Latest
Trending
Last reply 11 hours ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY A PAPER 2 (H432/02) - 21st June [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 2 (7405/2) - 18th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 1 (7405/1) - 10th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Higher Tier Triple (8462 1H) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 weeks ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (H432/01) - 10th June [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 (Foundation Combined) 8464/1F - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 (Foundation Combined) 8464/2F - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 Higher Tier Triple (8462 2H) - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Foundation Triple (8462 1F) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 5 Chem 2 Foundation - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 2 Chem 1 Foundation - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 months ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Sci Paper 2 Higher Tier (1SC0 2CH) - 13th Jun 2023 [Exam Chat]Trending
Last reply 11 hours ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY A PAPER 2 (H432/02) - 21st June [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 2 (7405/2) - 18th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 1 (7405/1) - 10th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Higher Tier Triple (8462 1H) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 weeks ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (H432/01) - 10th June [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 (Foundation Combined) 8464/1F - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 (Foundation Combined) 8464/2F - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 Higher Tier Triple (8462 2H) - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Foundation Triple (8462 1F) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 5 Chem 2 Foundation - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 2 Chem 1 Foundation - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 months ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Sci Paper 2 Higher Tier (1SC0 2CH) - 13th Jun 2023 [Exam Chat]



