AQA A Level Chemistry Paper 3 20th June 2018 Unofficial Markscheme
Scroll to see replies
How many marks would I lose on the 6 marker if I said keep the concentrations and volumes of B and C constant (tenchnically not true as volume should be varied) and if I only showed 1 graph of 1/t against initial concentration of A for first order only (no graph for zero or second order) although I did describe how to use the gradient to find the order?
Original post by DvsAmjed
How many marks would I lose on the 6 marker if I said keep the concentrations and volumes of B and C constant (tenchnically not true as volume should be varied) and if I only showed 1 graph of 1/t against initial concentration of A for first order only (no graph for zero or second order) although I did describe how to use the gradient to find the order?
I swear the volumes and concentrations of B, C and X should've been kept constant, but the volumes of water and A should've been changed?
Original post by mo08
I swear the volumes and concentrations of B, C and X should've been kept constant, but the volumes of water and A should've been changed?
Yes, but I didn’t mention how to vary the concentration of A or how to keep the overall volume constant. How many marks would I lose?
Original post by DvsAmjed
Yes, but I didn’t mention how to vary the concentration of A or how to keep the overall volume constant. How many marks would I lose?
I'm not entirely sure, sorry.
Original post by Lalalozzaland
How did everyone put to find initial rate in the 6 marker!? I put 1/time
I did that too!!! I think there was a mark for initial rate though because it said something about it in the question but i could not work out how to do it so idk
Original post by Cocovercoe
I did that too!!! I think there was a mark for initial rate though because it said something about it in the question but i could not work out how to do it so idk
if you use a colorimeter you can get a concentration against time curve from that you draw a tangent to the curve at time zero which will be your initial rate.
Original post by Alevelexperts
Be sure to rep @Bulletzone and @Tommy59375 and @Daniel100499 and @LunaCat and @eliza154 for contributions:
1.1 Explain...rate of reaction depends only on H+ Conc (2)
Since the other stuff were in excess you may assume that the concentration effectively shall remain constant. As a result the order of reaction with respect to those in excess shall be O as they shall have no effect on the rate of reaction/
1.2 What's done to each sample before titrated (2)
Can't remember this question
1.3 Explain...how graph shows order (2)
Because the graph is a straight line, the concentration of H+ is decreasing at a constant rate. Therefore the rate of reaction is constant (as this is one measure of rare kf reaction). Since the concentration of H+ doesn’t affect the rate of reaction, the order WRT H+ must be 0.
1.4 Calculate k1 and give units (3)
Gradient of graph / 0.05
k = 1.2x10^-3 Units: moldm-3s-1
1.5 Plot results (1)
Unless you can't count you'll probably get a mark.
1.6 Draw line of best fit (1)
The line of best fit shall vary quite a bit as there was a weak correlation.
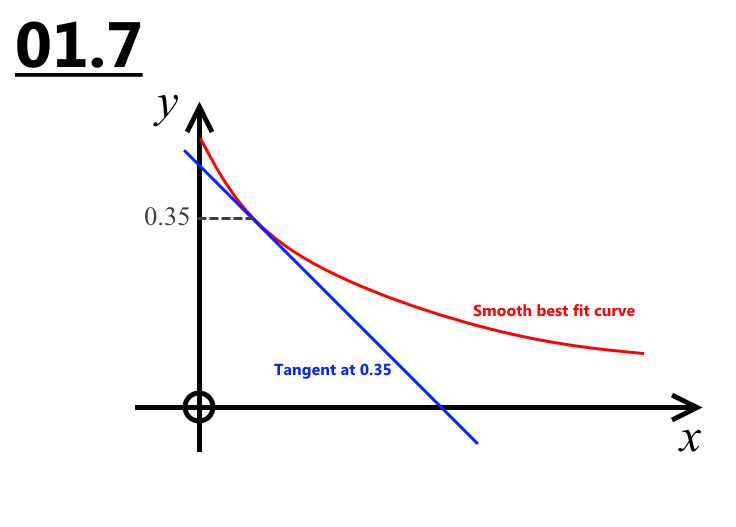
1.7 Calculate rate of reaction when H+ is 0.35 (2)
0.35 / (Time for your line of best fit)
rate = 4.4x10^-4
01.6 and 01.7 The LoBF should have been a smooth curve through all the points. The rate they wanted was equal to the gradient of the tangent to your curve at conc. = 0.35
1.8 Explain...series of experiments (6)
Cba
2.1 Sodium heated in Oxygen: Equation, Obs 1, Obs 2 (2)
4Na + O2 --------> 2Na2O (allow multiples) Yellow Glow and White solid produced
2.2 Phosphorus and Oxygen: Equation, Obs 1 (2)
P4 + 5O2 ------> P4O10 (Allow: 4P + 5O2 -----> P4O10) and White smoke
2.3 Explain....increase in MP from Sodium Oxide to Mg Oxide (2)
Magnesium has a higher charge density
so
Stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between the Mg2+ and O2- Ions.
Therefore more energy required to break the stronger ionic bond hence higher Melting point.
2.4 Explain....MP of oxide silicon higher than oxide of P (3)
Silicon Dioxide is a macromolecule.
It has Many strong covalent bonds (You need "many" for a mark)
Lots of energy needed to break the bonds.
P4O10 only has weaker Intermolecular forces between the molecules (van der waals forces), these are much weaker than the covalent bonds so less energy needed to break.
2.5 Describe....method for MP and how result for purity (3)
Fill 0. 5cm of powder if capillary tube
Place in meting point apparatus with thermometer attached
Increase temp slowly until powder has melted and rises up the tube
record temp
if lower than what data book says, then contained impurities
3.1 % yield of cyclohexane (3)
75.8%
3.2 Describe...test-tube reaction for cyclohexanol dehydrated. Observer what? (2)
Add bromine water.
Bromine water shall go from orange to colourless
3.3 Why Sodium carbonate used to wash (1)
Removes excess acid on surface of cyclohexene.
3.4 Important to open tap periodically (1)
Release the CO2 gas that is produced to prevent explosion.
3.5 Property of annhydrous calcium chloride (1)
Does not react with the product.
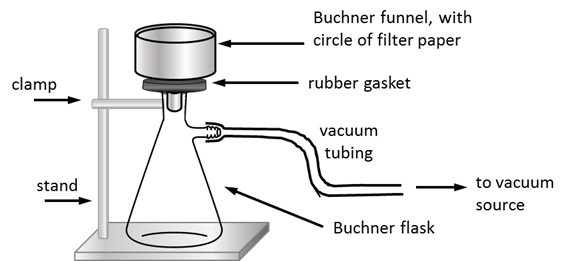
3.6 Describe apparatus used to remove drying agent under reduced pressure (2)
3.7 Explain....why cyclohexene has shorter retention time than cyclohexanol (2)
Cyclohexanol is more polar therefore it is more attracted/affinity to the silica (stationary phase) therefore takes longer to come out (Unsure about this)
3.8 Explain....infrared spectrum cyclohexene from chromotography did not contain cyclohexanol (1)
Contains C=C bond so shall have a peak at 1620-1680cm-1 (This may be wrong, quoting off memory)
No absorption in range 3250-3550 cm^-1
4.1 Temperature at 4th minute (5)

dT=2.1
4.2 Percentage uncertainty (1)
About 9.1%
Double the absolute uncertainty in the temperature readings because you’re making a subtraction between two readings and when you subtract or add two numbers you must add the absolute uncertainties on those numbers.
Then divide by the actual value for delta T and multiply by 100%
4.3 Suggest change to minimise heat loss (1)
Add a lid
4.4 Suggest another change to decrease uncertainty (2)
Need to increase the temperature change so have more concentrated reagents.
4.5 Equation between ethanedioic acid (25 cm3 0.80 moldm-3) and KOH (75 cm3 0.60 moldm-3) . Temp increase by 3.2. Calculate enthalphy change (5)
Equation is: HOOCCOOH + 2 KOH --> KOOCCOOK + 2 H2O
I will refer to ethanedioic acid as C2H2O4.
Initial moles of C2H2O4 = 25 × 10-3 × 0.80 = 0.02 mol
Initial moles of KOH = 75 × 10-3 × 0.60 = 0.045 mol
We can see from the equation that the reaction requires twice as much KOH as C2H2O4 but we've provided more than this amount. The KOH is in excess. All 0.02 mol of C2H2O4 will react. We can see that 0.04 mol of water will be produced.
Let m represent the mass of the solution.
m = density × volume
m = 1 × 100
m = 100 g
Let q represent the heat energy released from 100 cm3 of solution.
q = m c ∆T
q = 100 × 4.2 × 3.2
q = 1344 J
q = 1.344 kJ
So the heat energy released per mole of water is
1.344 ÷ 0.04 = 33.6 kJ mol-1
The process is exothermic so ∆H is negative.
∆H = -33.6 kJ mol-1
4.6 Suggest explanation for difference between -57kJ mol-1 and answer in 4.5 (2)
5. Both empirical and molecular (A: CH2O B: P4O10 C: NH2 D: CH3)
A
6. Correct bonding and bond polarity
A
7. He2+ particles (A: Gold atoms contain electrons B: Protons C: Neutrons D: Empty space)
D
8. Conclusion drawn Gold atoms have (A: small nucleus B: electrons in orbital C: ions in sea of e- D: more protons than He2+)
A
9. Termination step
D
10. Correct statement (A: HBr eletrophilic B: NaBH4 nucleophili addition-elimination C: KOH elimination D: KCN nucleophilic
C
11. Correct for 2-methylbutan 1 and 2-ol (A: formed by esters B: oxidised by reaction C: formed by hydration of 2-methylbut-2-ene D: four peaks)
A
12. Rate equation (A: k[w]2[x] B: k[w]2[y] C: k[x][y] D: k[x][z]
D
13. Graph with respect to conc of x
D It was curve that slopped upwards
14. Atomisation of iodine (A: 1/2I2(s) - I B: I2(s) - 2I C: 1/2I2(g) - I D: I2(g) - 2I)
A
15. Structure formed by aspartic acid
D, both COOH lost their Hydrogens
16. 13CNMR Peaks in 1-4 dimethylbenzene (A: 8 B: 4 C: 3 D: 2)
C
17. Highest MP (A: Al B: P C: Na D: S)
A
18. List of products (A: Sodium chloride, chlorate(I) and water B: Chlorate(I) and water C: Chloride, chlorate (V) and water D: Chloride and chlorate(I) )
A
19. Magnesium and steam (A: hydroxide and hydrogen B: hydroxide and oxygen C: oxide and hydrogen D: oxide and oxygen)
C
20: Observation (A: litmus paper red when touched B: paper blue when touched C: paper when when held above D: red litmus paper turns blue when held above)
D
21. Repeating unit of polymer pairs
It was C or B i think?
22. Structure of polyester soften at high temp (A: h bonds and van der waals B: dipole-dipole and van der waals C: carbon-carbon strong D: carbox-oxygen bonds)
B
23. Correct statement (A: HNO3 base B: catalyst C: electrophile D: reducing agent)
A
24. correct order of pH (A: am > eth > phe B: amm > phe > eth C: eth > amm > phe D: eth > phe > amm)
C
25. Ionic oxide strong alkalis (A: Al B: Mg C: Na D: S)
A
26. Correct statement (A: coordination no. decreases of cobalt B: Enthalpy change large and +ve C: entropy change large D: Shape of complex changes)
C
27. Which complex optical isomer
28. How many structural isomers react with tollens (A: 3 B: 4 C: 5 D: 6)
B
29. WHich ion cannot catalyse (A: Co2+ B: Cr2+ C: Fe2+ D@ Fe3+)
B
30. Shape influenced by presence of lone pairs (A: AlCl3 B: ClF3 C: IF6+ D: PCl6-)
B?
31. Greatest mass of solid Ba(OH)2 and (A: MgCl2 B: MgSO4 C: NaCl D: Na2SO4)
B
32. Which indicator methylamine (A: Thymol blue B: Bromophenol blue C: Phenol red D: Phenolphthalein)
B
33. Compound greatest percentage difference (A: CsF B: CsI C: LiF D: LiI)
D
34. Greatest equilibrium yield (A: high pr and high temp B: High pres and low temp C: low pres and high temp D: low pres and low temp)
C
1.1 Explain...rate of reaction depends only on H+ Conc (2)
Since the other stuff were in excess you may assume that the concentration effectively shall remain constant. As a result the order of reaction with respect to those in excess shall be O as they shall have no effect on the rate of reaction/
1.2 What's done to each sample before titrated (2)
Can't remember this question
1.3 Explain...how graph shows order (2)
Because the graph is a straight line, the concentration of H+ is decreasing at a constant rate. Therefore the rate of reaction is constant (as this is one measure of rare kf reaction). Since the concentration of H+ doesn’t affect the rate of reaction, the order WRT H+ must be 0.
1.4 Calculate k1 and give units (3)
Gradient of graph / 0.05
k = 1.2x10^-3 Units: moldm-3s-1
1.5 Plot results (1)
Unless you can't count you'll probably get a mark.
1.6 Draw line of best fit (1)
The line of best fit shall vary quite a bit as there was a weak correlation.
1.7 Calculate rate of reaction when H+ is 0.35 (2)
0.35 / (Time for your line of best fit)
rate = 4.4x10^-4
01.6 and 01.7 The LoBF should have been a smooth curve through all the points. The rate they wanted was equal to the gradient of the tangent to your curve at conc. = 0.35

1.8 Explain...series of experiments (6)
Cba
2.1 Sodium heated in Oxygen: Equation, Obs 1, Obs 2 (2)
4Na + O2 --------> 2Na2O (allow multiples) Yellow Glow and White solid produced
2.2 Phosphorus and Oxygen: Equation, Obs 1 (2)
P4 + 5O2 ------> P4O10 (Allow: 4P + 5O2 -----> P4O10) and White smoke
2.3 Explain....increase in MP from Sodium Oxide to Mg Oxide (2)
Magnesium has a higher charge density
so
Stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between the Mg2+ and O2- Ions.
Therefore more energy required to break the stronger ionic bond hence higher Melting point.
2.4 Explain....MP of oxide silicon higher than oxide of P (3)
Silicon Dioxide is a macromolecule.
It has Many strong covalent bonds (You need "many" for a mark)
Lots of energy needed to break the bonds.
P4O10 only has weaker Intermolecular forces between the molecules (van der waals forces), these are much weaker than the covalent bonds so less energy needed to break.
2.5 Describe....method for MP and how result for purity (3)
Fill 0. 5cm of powder if capillary tube
Place in meting point apparatus with thermometer attached
Increase temp slowly until powder has melted and rises up the tube
record temp
if lower than what data book says, then contained impurities
3.1 % yield of cyclohexane (3)
75.8%
3.2 Describe...test-tube reaction for cyclohexanol dehydrated. Observer what? (2)
Add bromine water.
Bromine water shall go from orange to colourless
3.3 Why Sodium carbonate used to wash (1)
Removes excess acid on surface of cyclohexene.
3.4 Important to open tap periodically (1)
Release the CO2 gas that is produced to prevent explosion.
3.5 Property of annhydrous calcium chloride (1)
Does not react with the product.
3.6 Describe apparatus used to remove drying agent under reduced pressure (2)

3.7 Explain....why cyclohexene has shorter retention time than cyclohexanol (2)
Cyclohexanol is more polar therefore it is more attracted/affinity to the silica (stationary phase) therefore takes longer to come out (Unsure about this)
3.8 Explain....infrared spectrum cyclohexene from chromotography did not contain cyclohexanol (1)
Contains C=C bond so shall have a peak at 1620-1680cm-1 (This may be wrong, quoting off memory)
No absorption in range 3250-3550 cm^-1
4.1 Temperature at 4th minute (5)
dT=2.1
4.2 Percentage uncertainty (1)
About 9.1%
Double the absolute uncertainty in the temperature readings because you’re making a subtraction between two readings and when you subtract or add two numbers you must add the absolute uncertainties on those numbers.
Then divide by the actual value for delta T and multiply by 100%
4.3 Suggest change to minimise heat loss (1)
Add a lid
4.4 Suggest another change to decrease uncertainty (2)
Need to increase the temperature change so have more concentrated reagents.
4.5 Equation between ethanedioic acid (25 cm3 0.80 moldm-3) and KOH (75 cm3 0.60 moldm-3) . Temp increase by 3.2. Calculate enthalphy change (5)
Equation is: HOOCCOOH + 2 KOH --> KOOCCOOK + 2 H2O
I will refer to ethanedioic acid as C2H2O4.
Initial moles of C2H2O4 = 25 × 10-3 × 0.80 = 0.02 mol
Initial moles of KOH = 75 × 10-3 × 0.60 = 0.045 mol
We can see from the equation that the reaction requires twice as much KOH as C2H2O4 but we've provided more than this amount. The KOH is in excess. All 0.02 mol of C2H2O4 will react. We can see that 0.04 mol of water will be produced.
Let m represent the mass of the solution.
m = density × volume
m = 1 × 100
m = 100 g
Let q represent the heat energy released from 100 cm3 of solution.
q = m c ∆T
q = 100 × 4.2 × 3.2
q = 1344 J
q = 1.344 kJ
So the heat energy released per mole of water is
1.344 ÷ 0.04 = 33.6 kJ mol-1
The process is exothermic so ∆H is negative.
∆H = -33.6 kJ mol-1
4.6 Suggest explanation for difference between -57kJ mol-1 and answer in 4.5 (2)
5. Both empirical and molecular (A: CH2O B: P4O10 C: NH2 D: CH3)
A
6. Correct bonding and bond polarity
A
7. He2+ particles (A: Gold atoms contain electrons B: Protons C: Neutrons D: Empty space)
D
8. Conclusion drawn Gold atoms have (A: small nucleus B: electrons in orbital C: ions in sea of e- D: more protons than He2+)
A
9. Termination step
D
10. Correct statement (A: HBr eletrophilic B: NaBH4 nucleophili addition-elimination C: KOH elimination D: KCN nucleophilic
C
11. Correct for 2-methylbutan 1 and 2-ol (A: formed by esters B: oxidised by reaction C: formed by hydration of 2-methylbut-2-ene D: four peaks)
A
12. Rate equation (A: k[w]2[x] B: k[w]2[y] C: k[x][y] D: k[x][z]
D
13. Graph with respect to conc of x
D It was curve that slopped upwards
14. Atomisation of iodine (A: 1/2I2(s) - I B: I2(s) - 2I C: 1/2I2(g) - I D: I2(g) - 2I)
A
15. Structure formed by aspartic acid
D, both COOH lost their Hydrogens
16. 13CNMR Peaks in 1-4 dimethylbenzene (A: 8 B: 4 C: 3 D: 2)
C
17. Highest MP (A: Al B: P C: Na D: S)
A
18. List of products (A: Sodium chloride, chlorate(I) and water B: Chlorate(I) and water C: Chloride, chlorate (V) and water D: Chloride and chlorate(I) )
A
19. Magnesium and steam (A: hydroxide and hydrogen B: hydroxide and oxygen C: oxide and hydrogen D: oxide and oxygen)
C
20: Observation (A: litmus paper red when touched B: paper blue when touched C: paper when when held above D: red litmus paper turns blue when held above)
D
21. Repeating unit of polymer pairs
It was C or B i think?
22. Structure of polyester soften at high temp (A: h bonds and van der waals B: dipole-dipole and van der waals C: carbon-carbon strong D: carbox-oxygen bonds)
B
23. Correct statement (A: HNO3 base B: catalyst C: electrophile D: reducing agent)
A
24. correct order of pH (A: am > eth > phe B: amm > phe > eth C: eth > amm > phe D: eth > phe > amm)
C
25. Ionic oxide strong alkalis (A: Al B: Mg C: Na D: S)
A
26. Correct statement (A: coordination no. decreases of cobalt B: Enthalpy change large and +ve C: entropy change large D: Shape of complex changes)
C
27. Which complex optical isomer
28. How many structural isomers react with tollens (A: 3 B: 4 C: 5 D: 6)
B
29. WHich ion cannot catalyse (A: Co2+ B: Cr2+ C: Fe2+ D@ Fe3+)
B
30. Shape influenced by presence of lone pairs (A: AlCl3 B: ClF3 C: IF6+ D: PCl6-)
B?
31. Greatest mass of solid Ba(OH)2 and (A: MgCl2 B: MgSO4 C: NaCl D: Na2SO4)
B
32. Which indicator methylamine (A: Thymol blue B: Bromophenol blue C: Phenol red D: Phenolphthalein)
B
33. Compound greatest percentage difference (A: CsF B: CsI C: LiF D: LiI)
D
34. Greatest equilibrium yield (A: high pr and high temp B: High pres and low temp C: low pres and high temp D: low pres and low temp)
C
For the cyclohexanol, cyclohexene question, I dont think you can say add bromine water. The question asked how could you tell that all of the alcohol had gone, but adding bromine water only tells you that ban alkene has formed, not that ALL of the alcohol has been dehydrated. I said acidified potassium dichromate because if any alcohol was present, it would go green
Original post by Success_Anyanwu
For the cyclohexanol, cyclohexene question, I dont think you can say add bromine water. The question asked how could you tell that all of the alcohol had gone, but adding bromine water only tells you that ban alkene has formed, not that ALL of the alcohol has been dehydrated. I said acidified potassium dichromate because if any alcohol was present, it would go green
exactly.... i gauged that question during the exam i said if you warm it withe acidified potassium dichromate and the color remained orange no alcohol was present. I mean, if the inital reaction just started and you poured bromine water in you would inevitably get a color change it doesnt indicate jack
Original post by Anonymouspsych
So now that we are done with chemistry, what are people's takes on what the grade boundaries will be for A*, A , B etc?
I think last year’s boundaries +/- 2 marks is a fair suggestion. Although I honestly think the difficulty was about the same except for the fact that I’ve seen a lot of people who hated paper 3
(edited 5 years ago)
Whats the answer for 1.2 and 4.6 pls???
Hi, does anyone have paper 3 from 2018? I want to do all of them for practice!
Quick Reply
Related discussions
- A-level Exam Discussions 2024
- GCSE Exam Discussions 2024
- A Level Exam Discussions 2023
- A Level Psychology Paper 2 (2023) Unofficial MarkScheme
- GCSE Exam Discussions 2023
- Aqa biology a level paper 3 2023
- oxfordAQA chemistry papers
- Gcse biology aqa exam paper 1 2023
- GCSE AQA Physics Paper 1 and 2 Revision and Study Chat
- AQA A-level Mathematics Paper 3 (7357/3) - 20th June 2024 [Exam Chat]
- AQA A-level Biology 7402 - Paper 2 - 13th June 2019
- AQA GCSE Biology Paper 1 (Higher Tier) 2022
- 2022 ocr as level chemistry papers
- AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 2 (7405/2) - 19th June 2023 [Exam Chat]
- Over 500 questions on AQA Bio Unit 4 + Current Spec and old Spec papers + MS!
- Edexcel IGCSE 24th May 2018 Paper 3H Unofficial mark Sceheme
- AQA A Level Mathematics Paper 3 (7357/3) - 20th June 2023 [Exam Chat]
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 1 [7th June 2023] Exam Chat
- A-level Chemistry Study Group 2022-2023
- Aqa Alevel chemistry paper 1 2023 unofficial markscheme
Latest
Trending
Last reply 2 days ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY A PAPER 2 (H432/02) - 21st June [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 2 (7405/2) - 18th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 1 (7405/1) - 10th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Higher Tier Triple (8462 1H) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 weeks ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (H432/01) - 10th June [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 (Foundation Combined) 8464/1F - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 (Foundation Combined) 8464/2F - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 Higher Tier Triple (8462 2H) - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Foundation Triple (8462 1F) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 5 Chem 2 Foundation - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 2 Chem 1 Foundation - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 months ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Sci Paper 2 Higher Tier (1SC0 2CH) - 13th Jun 2023 [Exam Chat]Trending
Last reply 2 days ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY A PAPER 2 (H432/02) - 21st June [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 2 (7405/2) - 18th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 1 week ago
AQA A-Level Chemistry Paper 1 (7405/1) - 10th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Higher Tier Triple (8462 1H) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 weeks ago
OCR A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (H432/01) - 10th June [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 (Foundation Combined) 8464/1F - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 (Foundation Combined) 8464/2F - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2 Higher Tier Triple (8462 2H) - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 2 weeks ago
AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Foundation Triple (8462 1F) - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 5 Chem 2 Foundation - 11th June 2024 [Exam Chat]Posted 3 weeks ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Paper 2 Chem 1 Foundation - 17th May 2024 [Exam Chat]Last reply 2 months ago
Edexcel GCSE Combined Sci Paper 2 Higher Tier (1SC0 2CH) - 13th Jun 2023 [Exam Chat]



