Post Your Economics Question Here
Scroll to see replies
A benefit of the informal sector in a LEDC- "Provides cheap inputs for the formal sector", would someone be able to explain this further please? Thanks!
What are the good things about unemployment? All I can think of is that it can help to keep the wage rate down.
What are the good things about inflation?
Why does a country want balance of payments equilibrium and not balance of payments surplus?
What are the benefits of international trade? What are the benefits of firms facing increased competition from firms internationally?
What fiscal policies can be used to reduce unemployment? I can think of a cut in income tax (to push up aggregate demand and make more people want to work) and a cut in unemployment benefits (to make the voluntary unemployed people want to work). But are these really correct? The second one looks wrong and seems more like a supply-side policy.
Thanks for any help.
What are the good things about inflation?
Why does a country want balance of payments equilibrium and not balance of payments surplus?
What are the benefits of international trade? What are the benefits of firms facing increased competition from firms internationally?
What fiscal policies can be used to reduce unemployment? I can think of a cut in income tax (to push up aggregate demand and make more people want to work) and a cut in unemployment benefits (to make the voluntary unemployed people want to work). But are these really correct? The second one looks wrong and seems more like a supply-side policy.
Thanks for any help.
gangsta316
What are the benefits of international trade? What are the benefits of firms facing increased competition from firms internationally?
What are the benefits of international trade? What are the benefits of firms facing increased competition from firms internationally?
I've just gone through this in my revision ha.
International trade will encourage comparitive advantage- more efficient use of the world resources and countries specialise in which they are most relatively efficient at with the lowest opportunity cost, this should increase output and employment leading to better standards of living etc
It'll also lead to greater choice and possibly lower prices for the consumer.
International competition could act as a discipline on domestic firm perhaps? Encourages them to be more productively efficient.
gangsta316
What are the good things about unemployment? All I can think of is that it can help to keep the wage rate down.
What are the good things about inflation?
Why does a country want balance of payments equilibrium and not balance of payments surplus?
What are the benefits of international trade? What are the benefits of firms facing increased competition from firms internationally?
What fiscal policies can be used to reduce unemployment? I can think of a cut in income tax (to push up aggregate demand and make more people want to work) and a cut in unemployment benefits (to make the voluntary unemployed people want to work). But are these really correct? The second one looks wrong and seems more like a supply-side policy.
Thanks for any help.
What are the good things about inflation?
Why does a country want balance of payments equilibrium and not balance of payments surplus?
What are the benefits of international trade? What are the benefits of firms facing increased competition from firms internationally?
What fiscal policies can be used to reduce unemployment? I can think of a cut in income tax (to push up aggregate demand and make more people want to work) and a cut in unemployment benefits (to make the voluntary unemployed people want to work). But are these really correct? The second one looks wrong and seems more like a supply-side policy.
Thanks for any help.
frictional unemployment is necessary for the economy as it ensures that the match between employer and employee is as good as possible. For example frictional unemployment is much higher for young people as they are still looking for the "right" job.
inflation helps fight wage rigidity. you may have a long term nominal wage contract. if the worker is not good you cant just lower his wage. so if there is inflation and you dont rais his nominal wage, then his real wage decreases. so in effect you are paying him less as you realised he is worth less.
hope that helps for those 2.
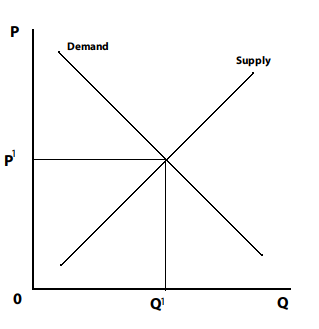
Hey. Quick question, how would one describe a diagram like this:
- Would you say equilibrium is at price P1 with Q1 demanded and supplied.
- Or equilibrium is at price 0P1 with 0Q1 demanded and supplied.
My economics teachers seem to keep saying it like the second version but I'd describe it like the first version.

The textbook seems to use both. Are both versions OK?
Thanks.
Greg.
Hey. Quick question, how would one describe a diagram like this:
- Would you say equilibrium is at price P1 with Q1 demanded and supplied.
- Or equilibrium is at price 0P1 with 0Q1 demanded and supplied.
My economics teachers seem to keep saying it like the second version but I'd describe it like the first version.
The textbook seems to use both. Are both versions OK?
- Would you say equilibrium is at price P1 with Q1 demanded and supplied.
- Or equilibrium is at price 0P1 with 0Q1 demanded and supplied.
My economics teachers seem to keep saying it like the second version but I'd describe it like the first version.

The textbook seems to use both. Are both versions OK?
Both are fine, and I also prefer the first one.
Thanks. 

Greg.
Hey. Quick question, how would one describe a diagram like this:
- Would you say equilibrium is at price P1 with Q1 demanded and supplied.
- Or equilibrium is at price 0P1 with 0Q1 demanded and supplied.
My economics teachers seem to keep saying it like the second version but I'd describe it like the first version.
The textbook seems to use both. Are both versions OK?
Thanks.

Hey. Quick question, how would one describe a diagram like this:
- Would you say equilibrium is at price P1 with Q1 demanded and supplied.
- Or equilibrium is at price 0P1 with 0Q1 demanded and supplied.
My economics teachers seem to keep saying it like the second version but I'd describe it like the first version.

The textbook seems to use both. Are both versions OK?
Thanks.
I've also wondered this. My teacher also seems to say the second one. I think it should be the first one because they're co-ordinates, not position vectors.
gangsta316
I've also wondered this. My teacher also seems to say the second one. I think it should be the first one because they're co-ordinates, not position vectors.
The second one is used to indicate distance, so you can be consistent in notation while make comparisons with distances which don't start at the origin. But it really doesn't matter, just use which one you prefer.
Say the exchange rate rose between pounds and dollars...does that mean that the price to buy a dollar in pounds has increased or vice versa?
gangsta316
I've also wondered this. My teacher also seems to say the second one. I think it should be the first one because they're co-ordinates, not position vectors.
Someone's been revising their physics/maths mechanics!

Jeester
Say the exchange rate rose between pounds and dollars...does that mean that the price to buy a dollar in pounds has increased or vice versa?
It depends on how you define the exchange rate. To be clearer I would say that an appreciation meant that pounds bought more dollars, while a depreciation meant that pounds bought less dollars. I think at A-level you would define the exchange rate as foreign/home (i.e. $/£), so an increase would be an appreciation and a decrease would be a depreciation (which kind of makes more sense than the other way round).
Examine the significance of an ageing population for both the labour markets (flexibility) and governments (public expenditures).
So far i've got tha there'll be an increase in government expenditure on pensions and there'll be more pressure on state health care budgets. I could see more employers opting out of employer contributing pension schemes. I'm not really sure about any other effects, especially flexibilty. Some ideas would be much appreciated. Thanks in advance
So far i've got tha there'll be an increase in government expenditure on pensions and there'll be more pressure on state health care budgets. I could see more employers opting out of employer contributing pension schemes. I'm not really sure about any other effects, especially flexibilty. Some ideas would be much appreciated. Thanks in advance
maltodextrin
Examine the significance of an ageing population for both the labour markets (flexibility) and governments (public expenditures).
So far i've got tha there'll be an increase in government expenditure on pensions and there'll be more pressure on state health care budgets. I could see more employers opting out of employer contributing pension schemes. I'm not really sure about any other effects, especially flexibilty. Some ideas would be much appreciated. Thanks in advance
So far i've got tha there'll be an increase in government expenditure on pensions and there'll be more pressure on state health care budgets. I could see more employers opting out of employer contributing pension schemes. I'm not really sure about any other effects, especially flexibilty. Some ideas would be much appreciated. Thanks in advance
Perhaps an increase in labour supply as people living longer would also suggest some people working for longer, especially if the retirement age is increased (I'm pretty sure this has already / is being done).
Where can i find info abt present unemployment level, inflation n interest rate and unemployment level of male and female?
And also why are females less likely to be unemployed and why is there a decrease in the no. of economically active men?
Thankyou
And also why are females less likely to be unemployed and why is there a decrease in the no. of economically active men?
Thankyou
bank of england website may be helpful.
With the aid of a diagram explain how the exchange rate is determined in a free market.
The mark scheme talks "both sides of the FOREX market" what is this?
Could you answer the question talking about interest rates, inflation and economic growth?
thanks
The mark scheme talks "both sides of the FOREX market" what is this?
Could you answer the question talking about interest rates, inflation and economic growth?
thanks
vinsta
With the aid of a diagram explain how the exchange rate is determined in a free market.
The mark scheme talks "both sides of the FOREX market" what is this?
Could you answer the question talking about interest rates, inflation and economic growth?
The mark scheme talks "both sides of the FOREX market" what is this?
Could you answer the question talking about interest rates, inflation and economic growth?
"FOREX market" = foreign exchange market, and by "both sides" I assume it means demand and supply. So it sounds like you'd draw the standard supply and demand diagram for the currency, than go on to discuss what might shift and supply and demand curves. Also by "free market" I would take that to mean floating exchange rates (as opposed to fixed).
well the exchange rate depends on the supply and demand for the currency. the supply is given by S-I the level of savings and investment in the economy, so yes interest rates. and yes inflation, because you can talk about how real exchange rate = nominal *P/P1 where P1 is price in other countries, so relative inflation rates matter.
both sides i dont know what is meant with though. i guess what i just said, supply and demand of the currency on the forex.
also yes economic growth as maybe u et more competitive so u exports more competitive so more demand for currency.
both sides i dont know what is meant with though. i guess what i just said, supply and demand of the currency on the forex.
also yes economic growth as maybe u et more competitive so u exports more competitive so more demand for currency.
What are capital outflows? Why would a developing country have capital outflows? Is it because of debt? Are they good or bad?
Quick Reply
Related discussions
- TSR Study Together - STEM vs Humanities!
- Edexcel A Level Economics A Paper 1 (9ECO 01) - 15th May 2024 [Exam Chat]
- A-level Economics Study Group 2023-2024
- Economics Application
- 2023 WJEC Ecomnomics A Level Grade Boundaries
- Eduqas A level Economics
- is 'taxi driver' classed as a job of a lower socio-economic background?
- Aqa Economics or Edexcel Politics or Aqa Sociology???
- alevel economics
- A-level Economics Study Group 2022-2023
- Official University of Roehampton Applicant Thread for 2024
- economics a level aqa
- Geography vs Economics A level choices
- Help me pick unis
- Economics at Aberdeen
- LSE Economics: without FurtherMaths
- GCSEs good enough for Econ and Econ history?
- Choosing Between Reading and Loughborough for Economics & Investment Banking
- IGCSE forum?
- Predictions for 2024 aqa alevel economics




